Why URL Structure Determines Digital Shelf Survival
How to optimize your Shopware URLs not just for Google, but for the next generation of AI agents and LLMs.
In the world of e-commerce, the playing field has fundamentally changed. For years, the mantra was: "Optimize for the user and for Google." But in 2025, there's a third crucial player visiting your store: Artificial Intelligence.
From ChatGPT plugins to Google SGE (Search Generative Experience) to autonomous shopping bots—machines read your store differently than humans. While a human might overlook a cryptic URL, for an AI it's a lost data point. Modern Shopware AI features increasingly rely on clean data structures to deliver accurate results.
This guide is different from standard tutorials. We won't just show you how to remove that annoying product ID from your Shopware 6 URLs. We'll explain how to build a Shopware URL structure that secures your rankings today while simultaneously making your store the perfect data source for the AI-powered future.
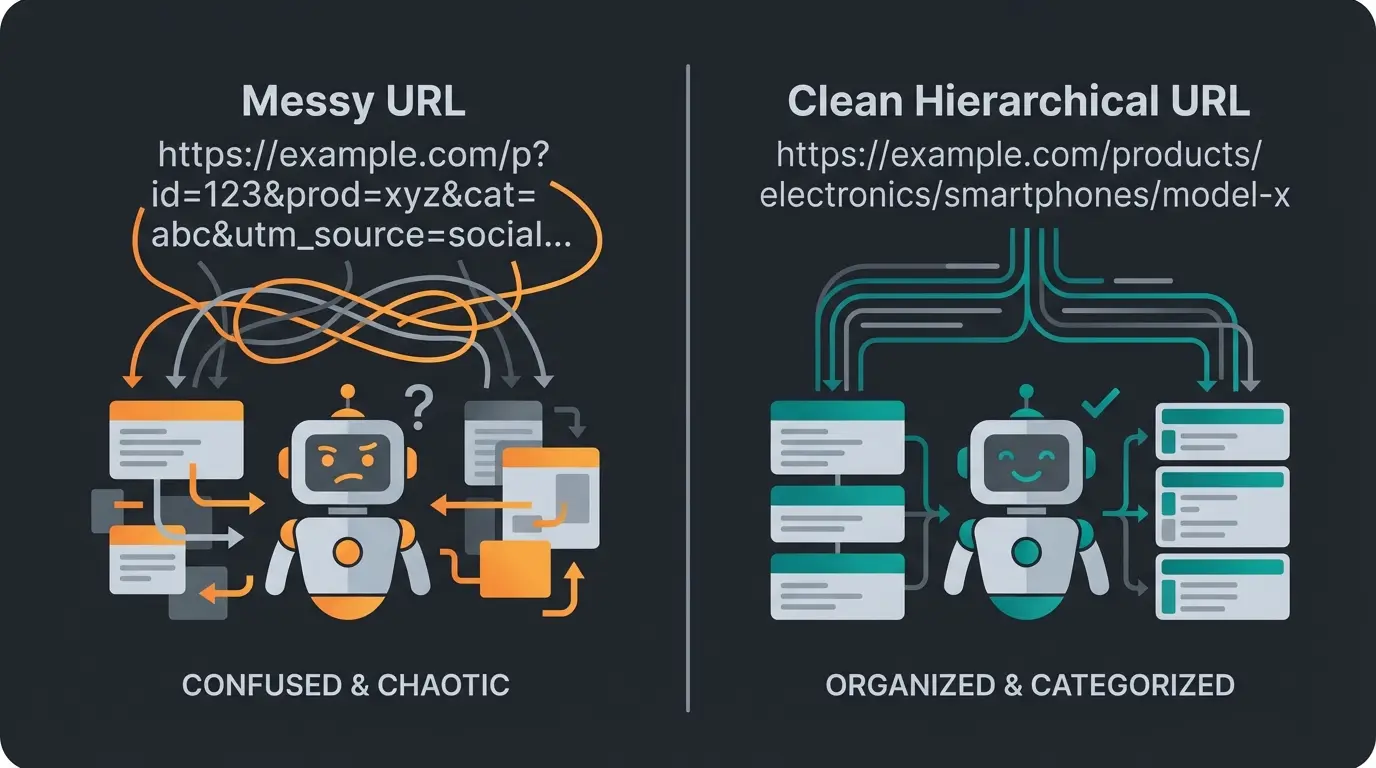
The Problem with Shopware's Default URLs
Before we dive into Twig templates, we need to clarify the "why." A URL is more than just an address; it's the first layer of information that any crawler (whether from Google or OpenAI) processes.
By default, Shopware 6 generates URLs that are "safe" but semantically weak. A typical URL looks like this:
`https://my-store.com/Product-Name/Product-Number`
Example: `https://my-store.com/Adidas-Ultraboost/SW10004`
Why this is problematic:
- SEO (Google): The product number (`SW10004`) provides no keyword value. It dilutes the URL's relevance.
- User Experience (UX): Users can't remember the URL, and it looks technical and unprofessional.
- AI Readability (The New Factor): A Large Language Model (LLM) crawling your store tokenizes the URL. `SW10004` gets broken down into meaningless tokens. The AI loses valuable context. A URL like `.../running-shoes/adidas/ultraboost-red` however delivers instant categorization to the AI: Category > Brand > Model > Attribute.
The Opportunity: Structure for Intelligence
When you optimize your Shopware URL structure, you're preparing your data for "Conversational Commerce." According to SearchAtlas, when a user asks an AI assistant: "Find me red running shoes from Adidas," the algorithm prioritizes sources whose structure it can interpret most easily. A clean URL acts like a "breadcrumb" for the AI, helping AI product finders deliver more accurate results.
Clean URLs show significantly higher click-through rates in search results
Semantic URLs enable AI agents to understand content without full page loads
Keyword-rich URLs contribute to improved search engine rankings
How Shopware 6 Generates URLs: The Fundamentals
To change the structure, we must understand how Shopware works under the hood. Shopware 6 uses a template system based on Twig, a flexible template engine for PHP.
The Technical Workflow
Understanding the URL generation process is crucial for effective optimization:
- The Template: You define a pattern in the backend (e.g., `{{ product.name }}`).
- The Generator: When a product is saved or the index is rebuilt, Shopware takes this pattern and fills it with the actual product data.
- The Database: The finished URL (the "slug") is stored in the `seo_url` table.
- The Router: When a customer calls the URL, Shopware looks up in this table which technical path (e.g., `/detail/12345`) this URL corresponds to.
According to Brocksi, this architecture allows for powerful customization while maintaining system performance through caching.
Where to Find the Settings
The path to better URLs is centralized in Shopware 6:
- Navigate to: Settings > Shop > SEO
- Here you'll find the SEO URL Templates section
You'll see templates for different entities:
- Product detail page
- Category page
- Landing page
The Perfect Product URL: Step-by-Step Optimization
The goal is a URL that is descriptive, hierarchically logical, and free of technical IDs.
Step 1: Understanding the Default Template
The default in Shopware is often:
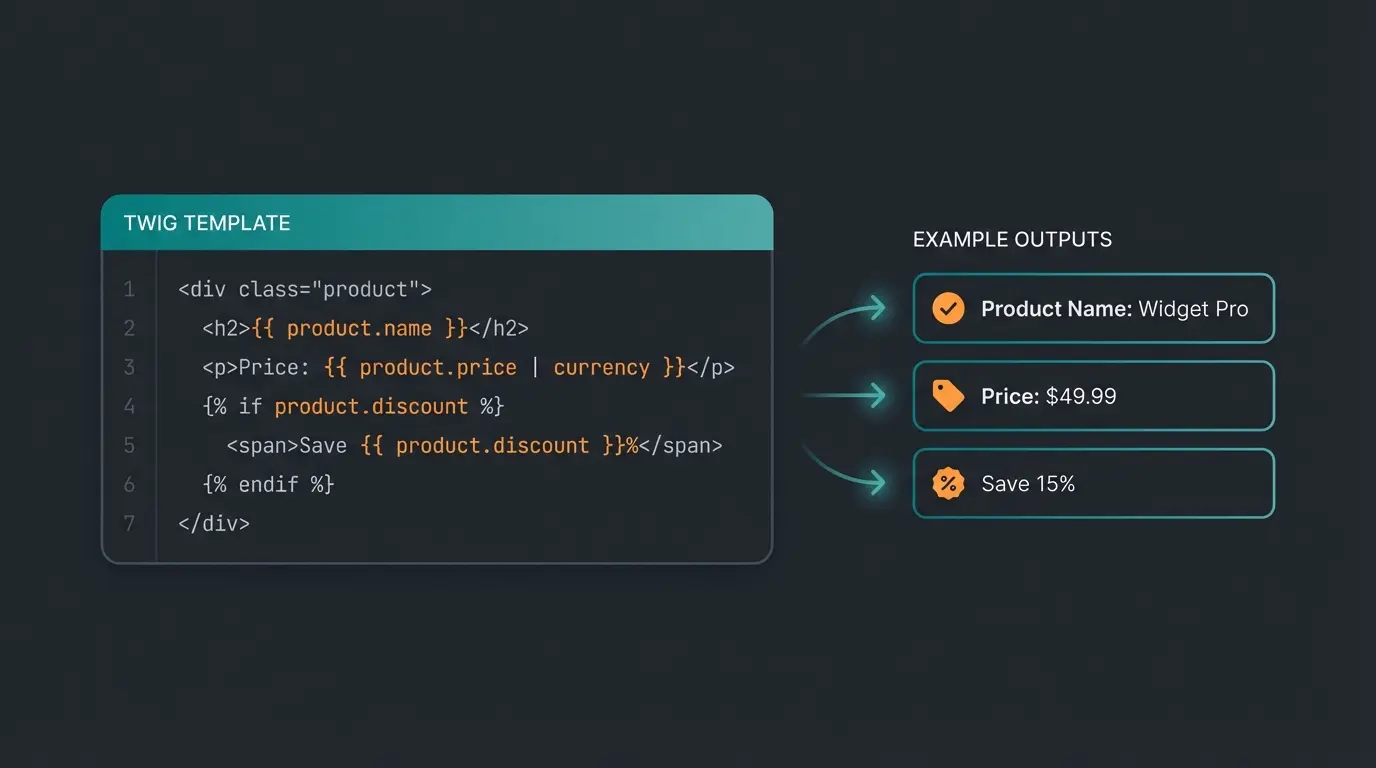
```twig {{ product.translated.name }}/{{ product.productNumber }} ```
This results in: `my-product/SW12345`.
Shopware does this for safety reasons: Product names are often not unique, but product numbers are. Without the number, two products named "Basic T-Shirt" could receive the same URL, leading to errors.
Step 2: The Golden Template for SEO & AI
For maximum readability, we want to remove the number and convert everything to lowercase.
The optimized template:
```twig {{ product.translated.name|lower }} ```
- `product.translated.name`: Takes the translated name (important for multilingual stores).
- `|lower`: A Twig filter that converts everything to lowercase (SEO best practice).
Result: `my-product`
Step 3: Avoiding the Uniqueness Trap
If you remove the product number, you must ensure that every product name is unique. If you have two products named "Summer Dress," Shopware will throw an error on the second product or (depending on the version) append a hash, which we want to avoid.
Strategy for AI Context:
To create uniqueness while simultaneously giving the AI more information, it's recommended to include attributes in the URL when names are generic. This approach enhances AI product consultation accuracy significantly.
Extended Template (Brand + Name):
```twig {{ product.manufacturer.translated.name|lower }}-{{ product.translated.name|lower }} ```
Result: `adidas-ultraboost`
This helps an AI agent immediately separate the brand entity ("Adidas") from the product ("Ultraboost"), even before the page content is loaded. As noted by Choto, this semantic clarity dramatically improves AI comprehension.
Review existing URL patterns and identify cryptic IDs or missing keywords
Create Twig template with product name, brand, or category hierarchy
Ensure all generated URLs will be unique to prevent conflicts
Save new template in Shopware SEO settings for each entity type
Execute CLI command to regenerate all SEO URLs with new structure
Confirm 301 redirects from old URLs are functioning correctly
Advanced: Variables, Logic, and Variant Handling
This is where the experts separate from the beginners. Simple stores use just the name. Smart stores use logic.
Conditional Logic with Twig (If-Statements)
Sometimes products don't have a manufacturer, or you want to change the URL structure based on certain criteria. Twig allows `if` queries directly in the SEO template field.
Scenario: If a manufacturer is stored, it should be in the URL. If not, only the product name.
```twig {% if product.manufacturer %} {{ product.manufacturer.translated.name|lower }}- {% endif %} {{ product.translated.name|lower }} ```
Single-line version:
```twig {% if product.manufacturer %}{{ product.manufacturer.translated.name|lower }}-{% endif %}{{ product.translated.name|lower }} ```
The Variant Dilemma: Own URL or Canonical?
Shopware 6 treats variants (e.g., Size L, Color Red) as separate entities. This often leads to duplicate content problems that affect both SEO and AI e-commerce transforms interpretation.
Option A: All Variants to the Main URL (SEO Focus)
Most SEO guides recommend not giving variants their own indexable URL or pointing all of them to the main product via canonical tag. According to GitHub discussions, this approach consolidates link equity effectively.
- Advantage: Maximum link power on one URL.
- Disadvantage: If a user (or AI) specifically searches for "Red Shoes," they land on the general page and must first click through.
Option B: Descriptive URLs for Variants (AI Focus)
For AI agents, precision is important. A URL like `.../t-shirt-basic-red-xl` is extremely valuable for an AI, as it directly confirms the attribute "Red" and "XL." This enhanced structure supports Shopware 6 chatbots in providing accurate product recommendations.
Recommendation:
Use a structure for variants that contains the distinguishing features, but strictly set the canonical tag in the frontend to the main product to avoid confusing Google.
Template for Variant URLs:
```twig {{ product.translated.name|lower }}- {% for option in product.options %} {{ option.translated.name|lower }}- {% endfor %} ```
This generates: `t-shirt-basic-red-xl-` (Note the trailing minus, which would need to be removed through advanced Twig slicing, or Shopware often cleans it up automatically).
Accessing Custom Fields
Do you have special data that's important for the URL (e.g., a series or collection) stored in a custom field (`customFields`)?
Syntax:
```twig {{ product.translated.customFields.technical_field_name|lower }} ```
Replace `technical_field_name` with the name you assigned in the backend under Settings > System > Custom Fields. According to Shopware documentation, custom fields offer extensive flexibility for URL customization, and Firebear Studio provides additional implementation examples.
Now that you understand URL structure optimization, see how our AI solution leverages clean data structures to deliver personalized product recommendations and boost conversions.
Start Free TrialTechnical Implementation: Indexes and Redirects
You've changed the template, but nothing happens on the frontend? This is the most common frustration moment in Shopware. Changes to templates do not automatically work retroactively.
The Indexer Process
Shopware doesn't recalculate URLs with every request (that would be too slow), but stores them in the database. When you change the template, you must force Shopware to recalculate all URLs.
1. The CLI Command (The Professional Way)
For large stores, don't rely on the button in the admin area. Use the console (SSH).
Execute this command in your store's main directory:
```bash php bin/console dal:refresh:index ```
```bash php bin/console dal:refresh:index --use-queue ```
This pushes the work into the queue, which is then processed by your workers.
2. Updating Only SEO URLs
The above command updates everything (prices, inventory, etc.). To save time, you can specifically target only the SEO index (depending on the Shopware version, flags may vary; often `--skip` helps to exclude other indexes). Great2Gether provides detailed documentation on index-specific commands.
301 Redirects and History
What happens to the old URLs (with ID)? Do they now lead to nowhere (404)?
No, if you've set it up correctly.
Shopware has a built-in redirect logic. When a URL is newly generated, the old URL isn't deleted from the database but marked as "no longer canonical." Shopware then automatically redirects via 301 Redirect from the old to the new URL. As shown in YouTube tutorials, this process maintains SEO equity effectively.
Checklist:
- Check the "Canonical URLs" option under Settings > Shop > SEO.
- Ensure old URLs aren't deleted but remain in the history.
Proper Shopware 6 support includes monitoring these redirects to prevent broken links.
The AI Advantage: Data Structure for the Future
Here's your competitive advantage. Most SEOs optimize URLs only for keywords. We optimize for understanding.
How LLMs "Read" URLs (Tokenization)
A Large Language Model doesn't read text word by word, but in "tokens" (syllables or word parts).
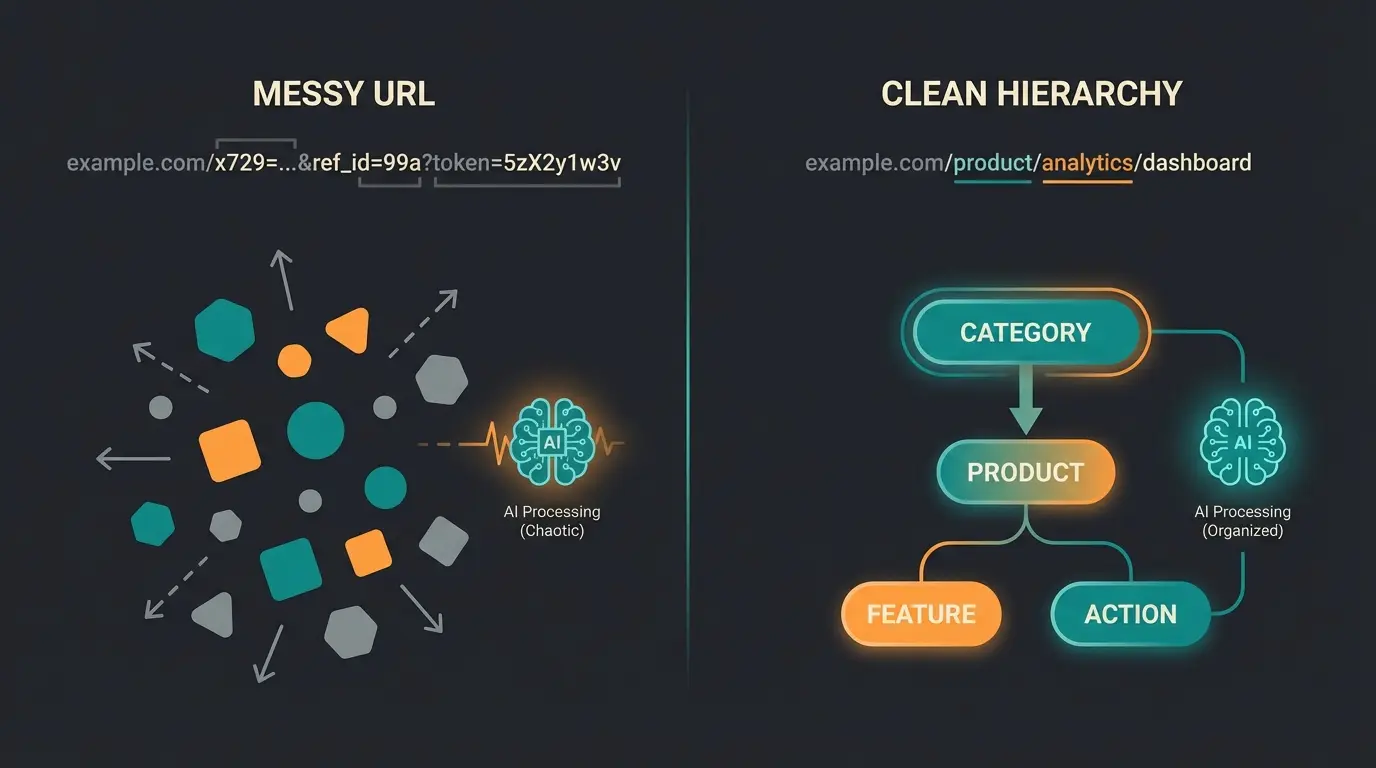
Bad URL: `/detail/018d45...`
- Tokens: `/`, `detail`, `/`, `018`, `d`, `45`...
- AI Interpretation: "A technical path to an object. Content unknown without crawling."
Good URL: `/mens/sneakers/nike/air-max-90`
- Tokens: `/`, `mens`, `/`, `sneakers`, `/`, `nike`, `/`, `air`, `-`, `max`, `-`, `90`
- AI Interpretation: "This is a product. Target audience: Men. Category: Sneakers. Brand: Nike. Model: Air Max 90."
This semantic clarity enables AI sales assistants to provide more accurate recommendations without parsing entire page contents.
Why Is This Important? (RAG & Crawl Budget)
In the future, AI agents (like Google Assistant or ChatGPT Search) will search websites live to generate answers (Retrieval Augmented Generation - RAG). This is why KI E-Commerce strategies must account for AI readability.
- Crawl Budget & Efficiency: AI crawlers are expensive to operate. They often decide based on the URL whether it's worth downloading and analyzing the page content at all. A descriptive URL signals high relevance.
- Hallucination Prevention: The more context the URL provides, the lower the probability that the AI misattributes the product.
- Filtering: When a user asks "Show me Nike shoes," the AI can filter URLs containing `/nike/` without having to open every page.
Strategy Tip:
Use the category hierarchy in the URL (`{{ category.path }}`) to teach the AI your store's taxonomy.
Template: `{{ category.path|lower }}/{{ product.translated.name|lower }}`
This approach transforms your store into an AI-powered consultation hub where intelligent systems can navigate your product catalog efficiently.
Cheat Sheet: Essential Twig Variables
For quick implementation, here are the most important building blocks for your templates. Copy these directly into your Shopware settings.
| Variable | Description | Example Output |
|---|---|---|
| {{ product.translated.name }} | The product name (translated) | Running Shoe Pro |
| {{ product.productNumber }} | The article number (SKU) | SW10004 |
| {{ product.manufacturer.translated.name }} | Manufacturer name | Adidas |
| {{ product.ean }} | The EAN/GTIN number | 40123456789 |
| {{ category.translated.name }} | Current category name | Sneakers |
| {{ product.translated.customFields.my_field }} | Custom field content | Summer Collection |
| |lower | Filter: Converts to lowercase | running shoe pro |
| |replace({' ': '-'}) | Filter: Replaces spaces with hyphens (Shopware usually does this automatically) | running-shoe-pro |
These variables form the foundation for both SEO optimization and enabling AI sales agents to parse your product data effectively.
Managing Multi-Channel URL Structures
Few resources go into depth on managing different URL structures for B2B vs. B2C channels within the same Shopware instance. This is a critical consideration for stores serving both markets.
Sales Channel-Specific Templates
Shopware 6 allows you to define different SEO templates for each sales channel. This is particularly valuable when:
- B2B customers need SKU numbers in URLs for procurement systems
- B2C customers prefer descriptive, marketing-friendly URLs
- Different language channels require different URL structures
According to Bay20, sales channel configuration significantly impacts SEO performance across different market segments. Firebear Studio also notes that proper multi-channel setup is essential for maintaining consistent AI data interpretation.
To configure channel-specific templates:
- Navigate to Settings > Shop > SEO
- Select the specific sales channel from the dropdown at the top
- Define your template for that channel
- Repeat for each sales channel
This granular control supports the AI Employee 'Kira' implementation, where different customer segments receive tailored experiences.
Impact on Crawl Budget for Large Stores
Advanced SEO topics like how bad URL structures waste crawl budget are critical for large shops with thousands of products.
Understanding Crawl Budget Waste
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages search engines (and AI agents) will crawl on your site within a given timeframe. Poor URL structures waste this precious resource:
- Duplicate content URLs: Variants without proper canonicals multiply crawl requirements
- Parameter-heavy URLs: Session IDs and tracking parameters create infinite URL combinations
- Non-semantic paths: Crawlers spend more time parsing URLs that don't reveal content type
Optimization Strategies for Large Catalogs
For stores with 10,000+ products, consider these approaches:
- Flat URL structure: Reduce hierarchy depth to minimize URL length
- Consistent patterns: Use identical template logic across all product types
- Strategic canonicalization: Point all variant URLs to parent products
- XML sitemap optimization: Prioritize main product URLs over variants
These optimizations not only improve SEO but also enhance how AI product consultation systems index and recommend your products.
Common Pitfalls & FAQ
Saving the template only changes the rule for the future. Existing products keep their old URL until the index is rebuilt. Solution: Execute `bin/console dal:refresh:index` via command line.
This is a classic SEO debate. Pro: More keywords, better structure for AI/bots (breadcrumb logic). Contra: If you move a product to a different category, the URL changes -> redirects -> loss of link power. Also, URLs are often too long. Recommendation: For maximum stability, keep the URL flat (`store.com/product-name`). For maximum AI comprehension, use hierarchies (`store.com/category/product-name`). A good compromise is often using only the main category or manufacturer.
Shopware uses `product.translated.name`. This means in the English sales channel, the English name is automatically used. Important: Make sure you check whether the template fits for each sales channel. You can select the sales channel at the top in the SEO module and define specific templates.
Shopware uses an internal "Slugify" service. Umlauts like "ä" are usually converted to "ae" or "a" (depending on settings). You usually don't need to worry about this in the template, but it's worth spot-checking the generated URLs.
Create descriptive URLs for variants that include distinguishing attributes (color, size) but set canonical tags to the main product. This gives AI agents precise data while consolidating SEO value. Example: `/t-shirt-basic-red-xl` canonicalized to `/t-shirt-basic`.
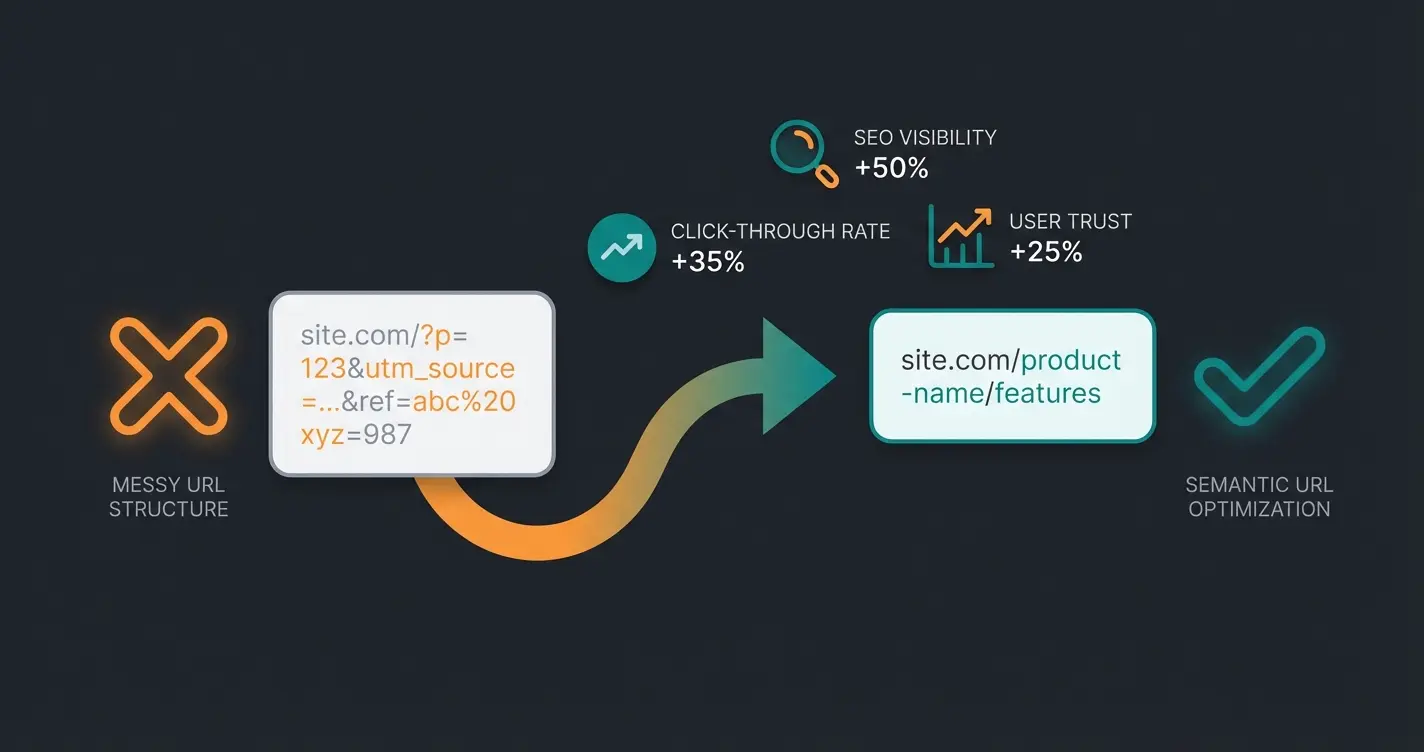
Conclusion: Clean URLs Are Business Intelligence
Optimizing your Shopware URL structure in 2025 is no longer a simple housekeeping task for the SEO intern. It's a strategic decision about how accessible your product data is to the outside world.
By switching from cryptic IDs (`/detail/123`) to semantic paths (`/manufacturer/product`), you kill two birds with one stone:
- You rank better on Google because keywords are in a prominent position and CTR (Click-Through Rate) is higher with descriptive URLs.
- You make your store "AI-Ready" by serving intelligent agents and bots structured data that they can understand without complex parsing.
Your next step:
Open your console, check your templates, and restart the index. Your data structure is the foundation for success in the age of artificial intelligence.
Your URL structure is now optimized for AI readability. Take the next step and implement AI-powered product consultation to transform how customers discover and buy your products.
Get Started Now